The Art of Black Lives Matter Activism: Part I
August 7, 2020
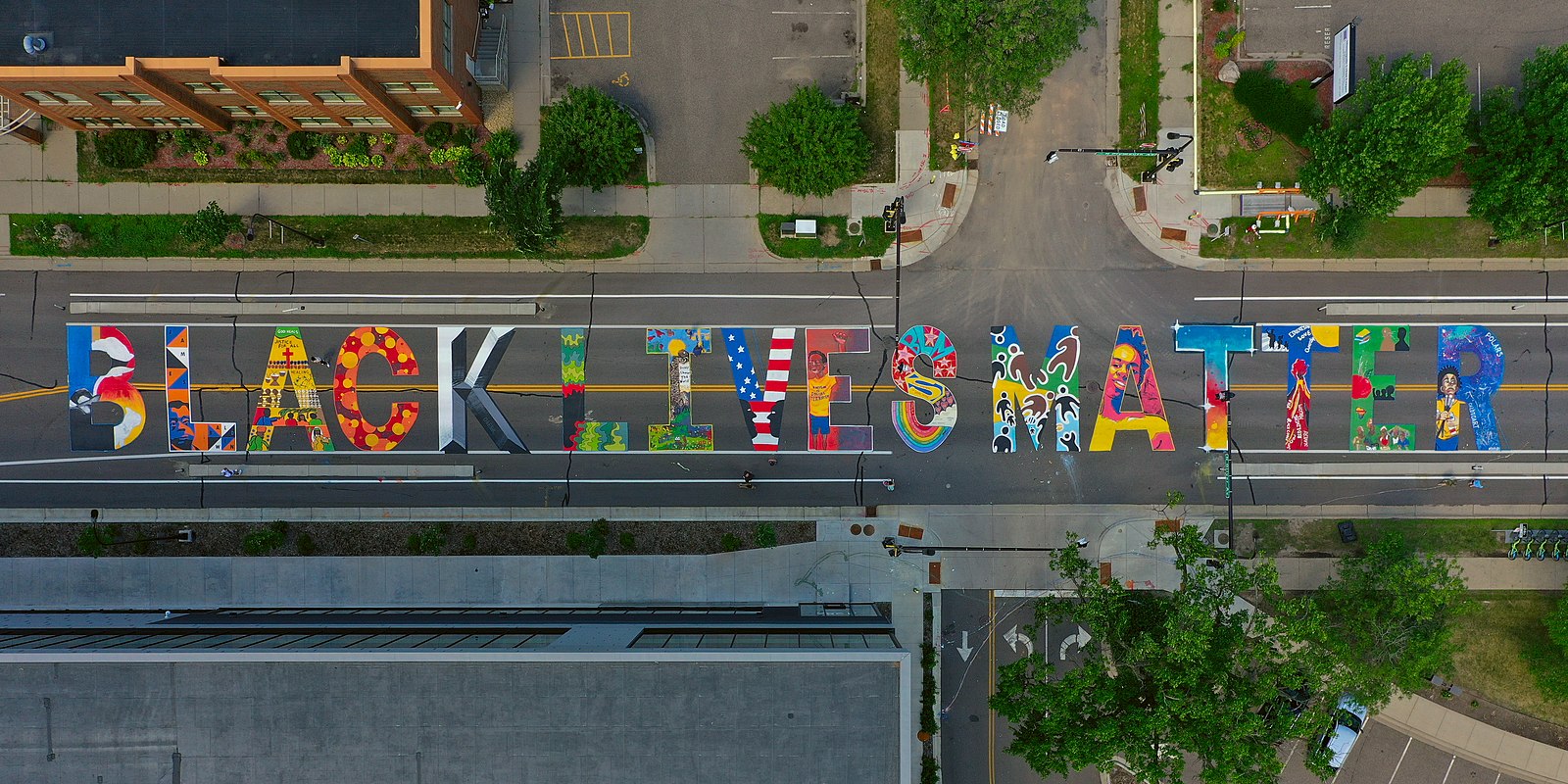
By Marla Katz
“The Art of Black Lives Matter Activism: Part I” will be followed by a second article, exploring the bail system, bail funds, and artists’ roles as philanthropists in the Black Lives Matter movement. Stay tuned!
“An artist’s duty, as far as I’m concerned, is to reflect the times.”
Nina Simone[1]
The Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution provides that no state shall enforce a law that “[denies] any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.”[2] The doctrine of equal protection requires the state to govern in an impartial manner, thus refraining from distinguishing between individuals based on differences that are “irrelevant to a legitimate governmental objective.”[3] In Strauder v. West Virginia (1880), the United States Supreme Court reasoned that the Fourteenth Amendment was meant to assure that Black people in the United States would receive the same protection of their civil rights as white people.[4] In 2020, 140 years after Strauder, the doctrine of equal protection is still being fought for as a critical means of protecting civil rights.
In spite of the Fourteenth Amendment guarantee of equal protection, a study published by Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences in August of 2019 suggests that the Fourteenth Amendment guarantee of equal protection has not been satisfied in terms of policing practices. The study—conducted by Frank Edwards, Hedwig Lee, and Michael Esposito—showed that Black people are at a disproportionate risk of being killed as a result of police violence. It showed that, among all social groups, Black men and boys face the highest risk of being killed during encounters with the police. Black men are about 2.5 times more likely to be killed by the police than white men. Similarly, Black women are about 1.4 times more likely to be killed by the police than white women.[5]
The recent murders of Breonna Taylor, George Floyd, Tony McDade, and other Black people by the police have caused a surge in the Black Lives Matter movement (the “Movement”). According to Pew Research Center, about two-thirds of U.S. adults support the Movement, with 38% of them claiming to “strongly support” it.[6] Support comes in different forms: from donating to organizations, to demonstrating, to producing art. Artists have represented the racial injustice propelling the Movement, as well as the manner in which the United States justice system fails Black people.

The Black Lives Matter Movement
#BlackLivesMatter was founded in 2013 in response to the acquittal of George Zimmerman, the neighborhood watch volunteer who fatally shot Trayvon Martin, an unarmed Black teenager, in Sanford, Florida. At the time of its founding by Patrisse Khan-Cullors, Alicia Garza, and Opal Tometi, Black Lives Matter represented a call to action. Black Lives Matter has now expanded into an international movement, representing a commitment to ending a system that adversely affects the social, economic, and political positions of Black people in the United States and allows the state to exert extreme, sometimes fatal, force against them.[7]
Though Black Lives Matter itself is not a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization, its foundation, Black Lives Matter Global Network Foundation, is. It is active in the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom, where it has received significant donations in support of the Movement. As a result, the Foundation recently announced a $6.5 million fund to support its affiliated chapters through unrestricted grant funding of up to $500,000 in multi-year grants.
It is apparent that the Black Lives Matter movement has received support on both national and global scales. In the United States and abroad, politicians, professional athletes, and celebrities have been seen supporting the Movement, as have lawyers and artists. In fact, artists have been instrumental to the Movement, taking on the roles of documentarians and critics.
Artists as Documentarians
According to a New York Times analysis, the Black Lives Matter movement may be the largest movement in United States history. The analysis states that, throughout the United States, there have been more than 4,700 demonstrations, or an average of 140 per day, since the first demonstrations began on May 26, 2020.[8] It is therefore understandable that institutions of art and cultural heritage have called for materials to document the Movement. For example, the New York Historical Society Museum and Library has asked the public to submit materials from New York and the surrounding region, explaining, “Future generations will want to understand what it was like to live through this period.”
Artists, specifically photographers, have proved critical to documenting the Movement in real time. Their photographs, often shared with the public through social media, are a testament to the nationwide scope of the Movement.
Montinique Monroe—a Black photojournalist based in Austin, Texas—has photographed the community response to the recent murder of George Floyd by Minneapolis police officers. Monroe photographed Floyd’s memorial service at the Fountain of Praise Church in Houston, Texas, as well as a candlelight vigil in his honor at his alma mater, Jack Yates High School. But, she photographed the events with particular pain. Monroe is the daughter of a Black man who was killed by a white police officer when she was just an infant. Monroe has explained that she is committed to telling her father’s story and the stories of other Black men, like Floyd, who died at the hands of police officers.[9]
Stephanie Mei-Ling—a black-American/Taiwanese photographer documenting cultural narratives and the complexities of intersectional identities—has also had a major part in photographing the Black Lives Matter movement. In a recent piece for High Country News, “Voices From an Uprising,” Mei-Ling compiled a series of portraits that she took at Black Lives Matter demonstrations in Los Angeles, California. A notable portrait, Nandi and Christopher, is paired with a statement by the subject: “I have a son, and African American men are targets.” Similarly, Mei-Ling has explained, “Black women have historically played critical roles in protest movements because racism and police brutality directly affect us. Not only are we being killed, but we are losing our fathers, our brothers, our husbands, and our sons.”[10] Mei-Ling thus reaffirms the beginnings of the Movement, as Black Lives Matter was founded by three Black female community organizers—Patrisse Khan-Cullors, Alicia Garza, and Opal Tometi.
The work of Monroe, Mei-Ling, and other photographers at the forefront of the Movement has allowed for real time documentation, as well as for the circulation of visual art. Their work has been circulated on social media, websites, and news outlets alike, alongside headlines about the Movement.
Artists as Critics
In addition to taking on the role of documentarians, artists are suited to be critics of the laws of the United States, specifically the laws dictating the justice system. A great number of artists—including Carlos Martiel, Jammie Holmes, and Kara Walker—represented the law before the Movement. But, the recent murders of Black people by the police have urged artists to denounce the failures of the law and to navigate the intersection of law and art.
Among other artists, Shaun Leonardo—a multidisciplinary artist known for negotiating “definitions surrounding black and brown masculinities”—has increasingly concentrated on the intersection of law and art throughout his career. Leonardo is the Lead Educator at Assembly, “an artist-led alternative to incarceration program offering long-term, paid training and pathways to creative employment for court-involved youth.” Outside of Assembly, Leonardo confronts urgent constitutional violations, such as the excessive use of force by the police, in his art. Though some of his art was produced before the current surge of the Black Lives Matter movement, its large-scale consumption has facilitated public education on the racial injustice propelling the Movement.
Shaun Leonardo tends to expose specific acts of police violence against Black men and boys in the United States. In February of 2015, in response to the chokehold death of Eric Garner, Leonardo began staging “I Can’t Breathe,” a performance and public workshop taking the form of a self-defense class. In art galleries, schools, and community centers alike, Leonardo taught participants self-protective strategies and more overt, defensive strategies. He specifically taught participants how to relieve the pressure of certain physical restraints, including the chokehold. Artnet News contributor Brian Boucher took part in the workshop, later noting, “The sadness and perhaps even impotence of the performance were poignantly clear when Leonardo pointed out that Garner himself used one of the evasive moves Leonardo was teaching…”[11] Boucher also noted that Leonardo repeated Garner’s last words, “I Can’t Breathe,” over ten times. Those last words are as grave now as they were then, as those are some of George Floyd’s last words.
Leonardo’s staging of “I Can’t Breathe” relates to the “self-defense” affirmative defense that is often used to justify the excessive use of force by the police. At the trial of George Zimmerman—the neighborhood watch volunteer who fatally shot Trayvon Martin, an unarmed Black teenager—Zimmerman was acquitted, likely under Florida’s “Stand-Your-Ground” law. The law allows a person to use force, even deadly force, if the person reasonably believes it is necessary to prevent death, serious bodily harm, or commission of a forcible felony. Although Zimmerman’s attorney did not raise a “Stand-Your-Ground” defense at the trial, a juror later admitted that jurors collectively discussed the law before finding Zimmerman not guilty.[12] In the pending trial regarding the death of George Floyd, former Minneapolis police officer J. Alexander Kueng—charged with aiding and abetting an unintentional second-degree murder and aiding and abetting second-degree manslaughter—“intends to rely upon” the Minnesota doctrines of self-defense, reasonable use of force, and authorized use of force.[13]
To circumvent disparities in criminal defenses across the United States, the federal Law Enforcement Misconduct Statute[14] enforces constitutional limits on conduct by law enforcement officers and the George Floyd Justice in Policing Act of 2020 (“the Act”) has the potential to do the same.[15] The House of Representatives introduced the Act on June 8, 2020 with the general intentions of “[increasing] accountability for law enforcement misconduct, [enhancing] transparency and data collection, and [eliminating] discriminatory policing practices.”[16] The Act would require law enforcement officers and agencies to be trained on implicit bias and racial profiling, to wear body cameras, and to report data on use-of-force incidents. It prods federal enforcement of constitutional violations by state and local law enforcement.
In addition to his performance art, Leonardo produced a series of drawings depicting scenes of the murders of Eric Garner, Michael Brown, Laquan McDonald, Tamir Rice, and other Black men and boys. His drawings were to be exhibited in Shaun Leonardo: The Breath of Empty Space at the Museum of Contemporary Art Cleveland (MoCa) from June 5, 2020 to September 6, 2020. But, three months before the exhibition was scheduled to begin, it was canceled due to “troubling community response.”[17] Among those community members that opposed the exhibition were Amanda King—a Black, Cleveland-based artist and activist—and Samaria Rice. King has collaborated with Ms. Rice since a Cleveland police officer killed her 12-year-old son, Tamir, in a park, thinking that his replica airsoft gun was real.
In a recent open letter, King explained that, since 2014, she and Ms. Rice have worked to confront the “appropriation and misuse of Tamir’s likeness by artists and cultural institutions.” In addition, King stressed the need for “an ethical balance between artistic expression and the potential harm to others, particularly those most affected, like the victims’ loved ones…” According to King, without such balance, artists and the institutions exhibiting their work risk re-traumatizing those most affected and the community at large.[18]
Following the exhibition’s cancellation, Leonardo responded that MoCa never gave him the opportunity to participate in community outreach. He also responded that “institutional white fragility led to an act of censorship.”[19] MoCa then apologized to Leonardo, the curator John Chaich, and members of the public. In its statement of apology, MoCa did not concede that it censored Leonardo’s art; rather, it acknowledged that, by canceling Leonardo’s exhibition, it prevented itself and its community members from having the “difficult and urgent conversations” that the exhibition stimulated.[20]
Artists as Ambassadors
Though artists like Leonardo produce art to further the Black Lives Matter movement, some artists are solicited to produce Black Lives Matter-related content to help major companies save face. For example, on June 3, 2020, Shantell Martin—a visual artist and cultural facilitator—received an email from an Art Producer at M:United, a branch within the advertising firm McCann. The Producer expressed interest in commissioning a mural on the boards protecting Microsoft’s Fifth Avenue location in Manhattan. The Producer made clear that the mural was time-sensitive, and it should be completed “while the protests [were] still relevant and the boards [were] still up.”[21]
The incident involving Martin exposed companies’ main motive in commissioning art: “wanting to soften the brutal optics of its own self-interest.”[22] Companies feared that having blank boards during the peak of the Movement would turn away potential customers. As a result, companies began soliciting artists to produce Black Lives Matter-related art, thus showing their supposed commitment to corporate social responsibility. But, it is arguable that commissioning art is nothing more than a quick fix, creating the illusion of solidarity in the Movement and enhancing the aesthetic of the otherwise dull storefronts.
Like companies, cities throughout the United States, such as New York and Washington D.C., have initiated public art projects in response to the Movement. On July 9, 2020, New York began painting “Black Lives Matter” in large yellow letters on Fifth Avenue, between 56th and 57th Streets, in Manhattan—right outside of Trump Tower. New York City Mayor Bill de Blasio backed the project and joined city workers and community members in its completion. But, the project has been called “the latest flare-up in a yearslong feud” between President Trump and Mayor de Blasio,[23] suggesting that perhaps Mayor de Blasio had an ulterior motive. The project has led to the notion that, while the power of public art is great, it does not excuse the government or governmental officials from enforcing policy reform in the communities where the public art is featured.
As public art continues to emerge on boarded storefronts, buildings, and streets across the United States, it is unclear whether it will be protected from defacement or destruction under the Visual Artists Rights Act of 1990 (“VARA”),[24] as interpreted in the pending 5Pointz case.[25]
One Thing is Clear…
Whether acting as documentarians or critics, artists have contributed much to the Black Lives Matter movement. As Aaron Bryant—curator at the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture—has said, “Artists have always been at the lead of protest, resistance, and hope in Black communities and other marginalized communities across the country.”[26]
Additional Readings:
- The Guardian, Capturing the Cry for Change: Photographers on the BLM Protests, https://www.theguardian.com/media/2020/jun/12/capturing-the-cry-for-change-photographers-on-the-blm-protests.
- Max Lakin, When Luxury Stores Decorate Their Riot Barricades With Protest Art, N.Y. Times (June 22, 2020) https://www.nytimes.com/2020/06/22/opinion/corporate-brands-protest-art.html.
- Carly Mallenbaum, Art Activism: Stories Behind Murals, Street Paintings and Portraits Created in Protest, USA Today (July 6, 2020) https://www.usatoday.com/in-depth/life/2020/06/22/protest-art-stories-behind-moving-images-demand-change/3195704001/.
- Deidre McPhillips, Deaths From Police Harm Disproportionately Affect People of Color, U.S. News & World Report (June 3, 2020) https://www.usnews.com/news/articles/2020-06-03/data-show-deaths-from-police-violence-disproportionately-affect-people-of-color.
- Seph Rodney, An Artist Teaches Us How to Breathe Under Duress, Hyperallergic (Mar. 7, 2017) https://hyperallergic.com/362098/an-artist-teaches-us-how-to-breathe-under-duress.
- Laura Beltrán Villamizar, As Black Photographers Document Protests, They Tell Their ‘Own History In Real Time’, NPR (June 13, 2020) https://www.npr.org/sections/pictureshow/2020/06/13/873427617/as-black-photographers-document-protests-they-tell-their-own-history-in-real-tim.
About the Author: Marla Katz is a Summer 2020 Legal Intern for the Center for Art Law. She earned a B.A. and M.A. in English from St. John’s University. She is now a student at the University of Connecticut School of Law, where she is a member of the Connecticut Law Review and the current President of UConn Law’s Arts, Entertainment, and Sports Law Society. She can be reached at marla.katz@uconn.edu.
- Nina Simone: An Artist’s Duty, YouTube (Feb. 21, 2013), https://youtu.be/99V0mMNf5fo. ↑
- U.S. Const. amend. XIV. ↑
- Legal Information Institute, Equal Protection, https://www.law.cornell.edu/wex/equal_protection (last visited July 13, 2020). ↑
- Strauder v. West Virginia, 100 U.S. 303, 306–07 (1880). ↑
- Frank Edwards et al., Risk of Being Killed by Police Use of Force in the United States by Age, Race–Ethnicity, and Sex, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (Aug, 20, 2019) https://www.pnas.org/content/116/34/16793.full. ↑
- Kim Parker et al., Amid Protests, Majorities Across Racial and Ethnic Groups Express Support for the Black Lives Matter Movement, Pew Research Center (June 12, 2020) https://www.pewsocialtrends.org/2020/06/12/amid-protests-majorities-across-racial-and-ethnic-groups-express-support-for-the-black-lives-matter-movement/. ↑
- Black Lives Matter, About, https://blacklivesmatter.com/about/ (last visited July 10, 2020). ↑
- Larry Buchanan et al., Black Lives Matter May Be the Largest Movement in U.S. History, N.Y. Times (July 3, 2020) https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/07/03/us/george-floyd-protests-crowd-size.html. ↑
- Laura Beltrán Villamizar, As Black Photographers Document Protests, They Tell Their ‘Own History In Real Time’, NPR (June 13, 2020) https://www.npr.org/sections/pictureshow/2020/06/13/873427617/as-black-photographers-document-protests-they-tell-their-own-history-in-real-tim. ↑
- Id. ↑
- Artnet News, artnet News Critics’ Picks: The Most Memorable Artworks of 2016 (Dec. 19, 2016) https://news.artnet.com/opinion/most-memorable-artworks-2016-776054. ↑
- Glenn Kessler, Was the ‘Stand Your Ground’ Law the ‘Cause’ of Trayvon Martin’s Death?, Washington Post (Oct. 29, 2014), https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/fact-checker/wp/2014/10/29/was-the-stand-your-ground-law-the-cause-of-trayvon-martins-death/. ↑
- Aaron Keller, Ex-Minneapolis Cop Charged in George Floyd Death Plans to Argue Self Defense, Reasonable Use of Force at Trial: Documents, Law & Crime (June 29, 2020), https://lawandcrime.com/george-floyd-death/ex-minneapolis-cop-charged-in-george-floyd-death-plans-to-argue-self-defense-reasonable-use-of-force-at-trial-documents/. ↑
- 18 U.S.C. § 242. ↑
- H.R. 7120, 116th Cong. (2019-2020). ↑
- Id. ↑
- Museum of Contemporary Art Cleveland, Statement sent to Shaun Leonardo, March 2020, https://www.mocacleveland.org/exhibitions/shaun-leonardo-breath-empty-space (last visited July 10, 2020). ↑
- Amanda D. King, Artist Activist Amanda D. King Addresses MoCa Cleveland’s Cancellation of Exhibition on Police Brutality, Open Letter to Arts & Activism Community, https://amandadking.weebly.com/ (last visited July 14, 2020). ↑
- Museum of Contemporary Art Cleveland, Sean Leonardo’s note, posted with permission (June 6, 2020) https://www.mocacleveland.org/mocas-apology-artist-shaun-leonardo. ↑
- Museum of Contemporary Art Cleveland, Our apology to artist Shaun Leonardo (June 7, 2020) https://www.mocacleveland.org/mocas-apology-artist-shaun-leonardo. ↑
- Shantell Martin (@shantell_martin), Instagram (June 6, 2020) https://www.instagram.com/p/CBGn0IXA9Q9/?utm_source=ig_web_copy_link. ↑
- Max Lakin, When Luxury Stores Decorate Their Riot Barricades With Protest Art, N.Y. Times (June 22, 2020) https://www.nytimes.com/2020/06/22/opinion/corporate-brands-protest-art.html. ↑
- Michael Gold & Daniel E. Slotnik, N.Y.C. Paints ‘Black Lives Matter’ in Front of Trump Tower, N.Y. Times (July 9, 2020) https://www.nytimes.com/2020/07/09/nyregion/blm-trump-tower.html. ↑
- Blake Brittain, Protest Art Fate Tied to Obscure, Rarely Litigated Copyright Law, Bloomberg Law (July 16, 2020), https://news.bloomberglaw.com/ip-law/protest-art-fate-tied-to-obscure-rarely-litigated-copyright-law. ↑
- Castillo v. G&M Realty L.P., No. 18-498 (2d Cir. 2020). ↑
- Carly Mallenbaum, Art Activism: Stories Behind Murals, Street Paintings and Portraits Created in Protest, USA Today (July 6, 2020) https://www.usatoday.com/in-depth/life/2020/06/22/protest-art-stories-behind-moving-images-demand-change/3195704001/. ↑
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and is not meant to provide legal advice. Readers should not construe or rely on any comment or statement in this article as legal advice. For legal advice, readers should seek a consultation with an attorney.



You must be logged in to post a comment.